 Jul 10,2018
Jul 10,2018
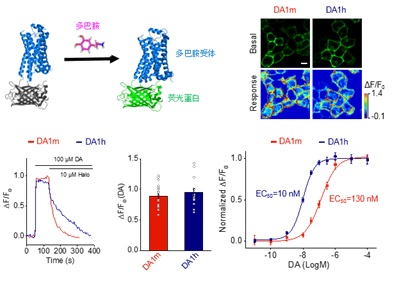
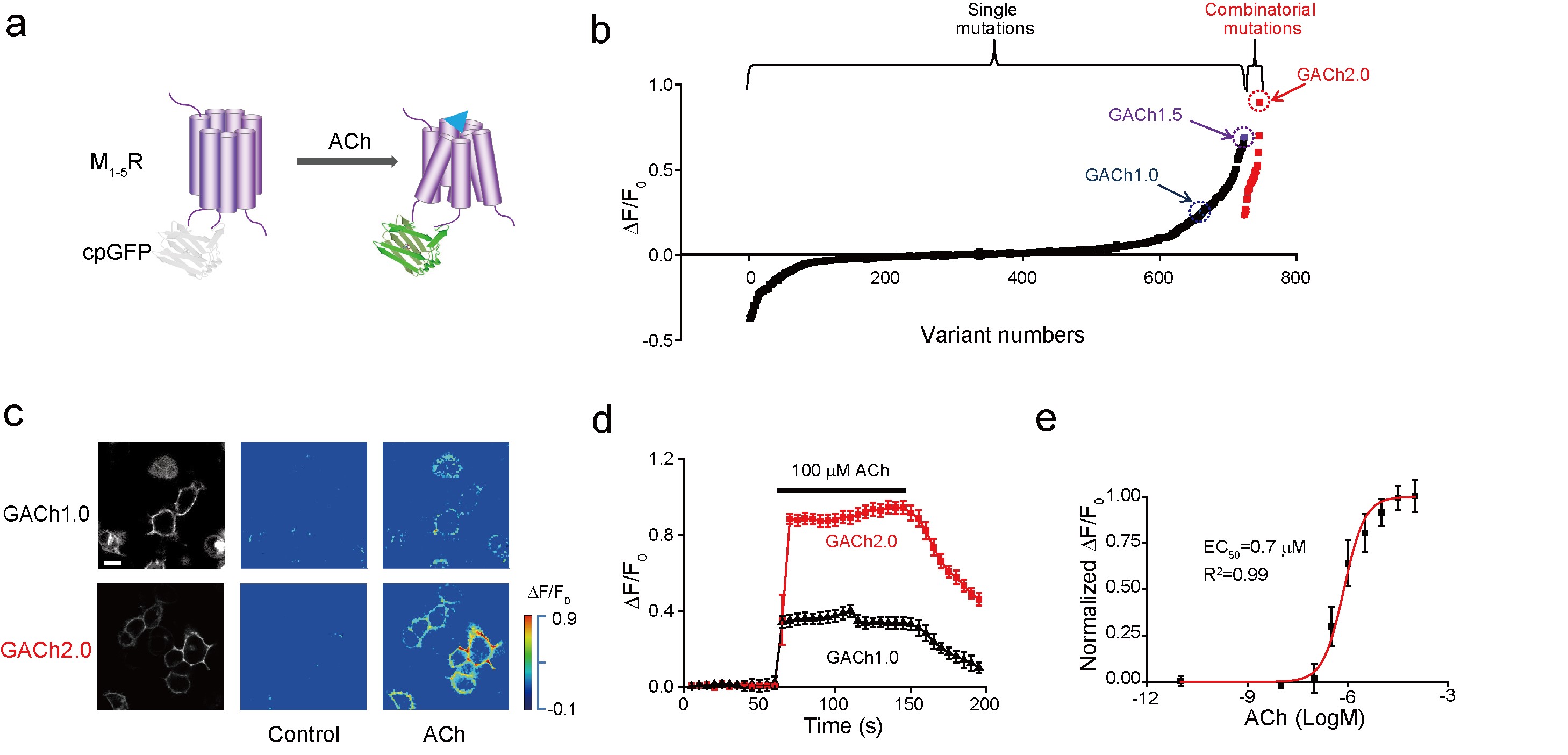
The neurotransmitter acetylcholine (ACh) regulates a diverse array of physiological processes throughout the body. Despite its importance, cholinergic transmission in the majority of tissues and organs remains poorly understood owing primarily to the limitations of available ACh-monitoring techniques. We developed a family of ACh sensors (GACh) based on G-protein-coupled receptors that has the sensitivity, specificity, signal-to-noise ratio, kinetics and photostability suitable for monitoring ACh signals in vitro and in vivo. GACh sensors were validated with transfection, viral and/or transgenic expression in a dozen types of neuronal and non-neuronal cells prepared from multiple animal species. In all preparations, GACh sensors selectively responded to exogenous and/or endogenous ACh with robust fluorescence signals that were captured by epifluorescence, confocal, and/or two-photon microscopy. Moreover, analysis of endogenous ACh release revealed firing-pattern-dependent release and restricted volume transmission, resolving two long-standing questions about central cholinergic transmission. Thus, GACh sensors provide a user-friendly, broadly applicable tool for monitoring cholinergic transmission underlying diverse biological processes.
 Jun 26,2018
Jun 26,2018
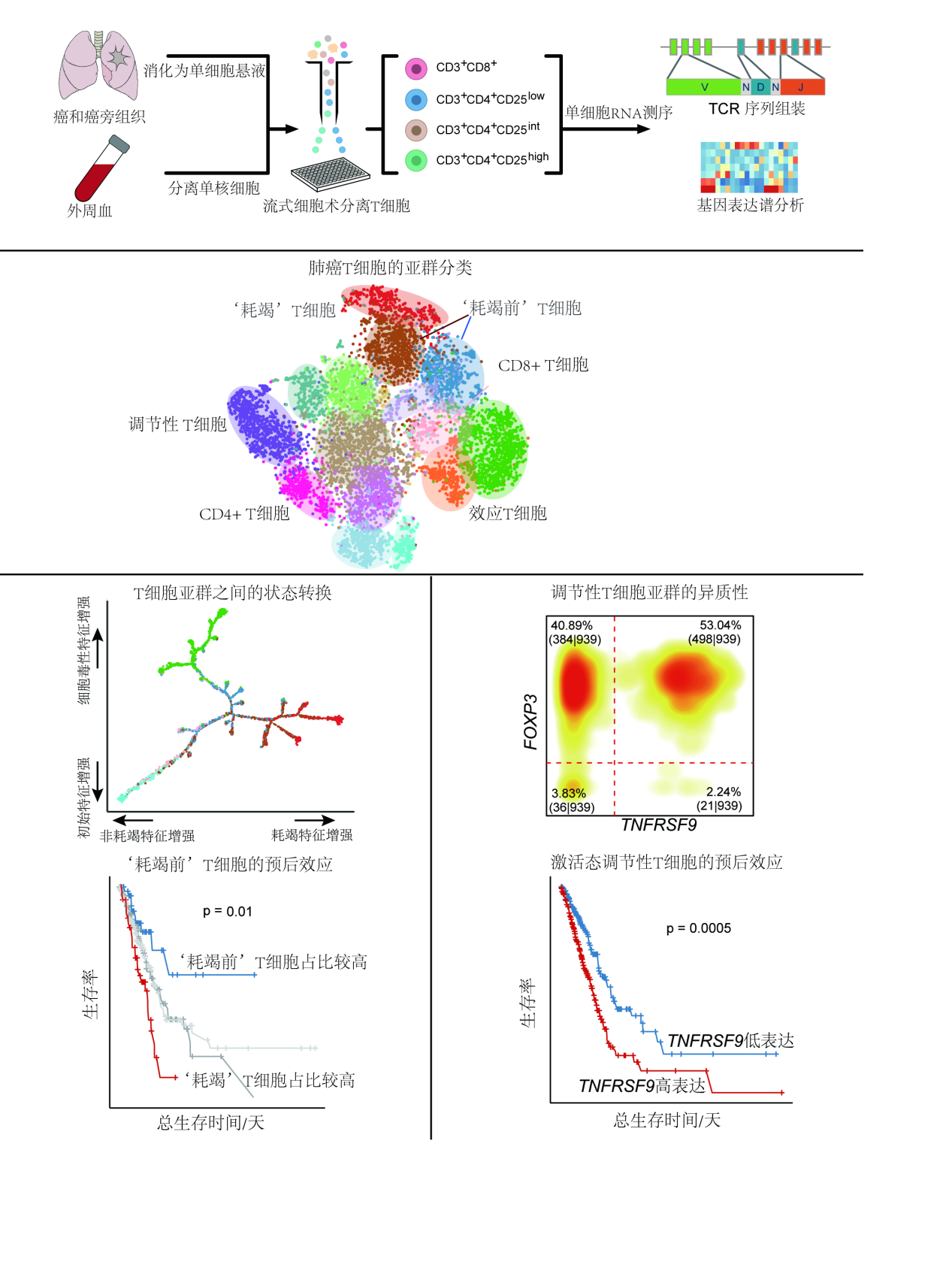
Cancer immunotherapies have shown sustained clinical responses in treating non-small-cell lung cancer, but efficacy varies and depends in part on the amount and properties of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes. To depict the baseline landscape of the composition, lineage and functional states of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes, here we performed deep single-cell RNA sequencing for 12,346 T cells from 14 treatment-naïve non-small-cell lung cancer patients. Combined expression and T cell antigen receptor based lineage tracking revealed a significant proportion of inter-tissue effector T cells with a highly migratory nature. As well as tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells undergoing exhaustion, we observed two clusters of cells exhibiting states preceding exhaustion, and a high ratio of “pre-exhausted” to exhausted T cells was associated with better prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma. Additionally, we observed further heterogeneity within the tumor regulatory T cells (Tregs), characterized by the bimodal distribution of TNFRSF9, an activation marker for antigen-specific Tregs. The gene signature of those activated tumor Tregs, which included IL1R2, correlated with poor prognosis in lung adenocarcinoma. Our study provides a new approach for patient stratification and will help further understand the functional states and dynamics of T cells in lung cancer.
 Jun 19,2018
Jun 19,2018
DNA methylation, chromatin states and their interrelationships represent critical epigenetic information, but these are largely unknown in human early embryos. Here, we apply single-cell chromatin overall omic-scale landscape sequencing (scCOOL-seq) to generate a genome-wide map of DNA methylation and chromatin accessibility at single-cell resolution during human preimplantation development. Unlike in mice, the chromatin of the paternal genome is already more open than that of the maternal genome at the mid-zygote stage in humans, and this state is maintained until the 4-cell stage. After fertilization, genes with high variations in DNA methylation, and those with high variations in chromatin accessibility, tend to be two different sets. Furthermore, 1,797 out of 5,155 (35%) widely open chromatin regions in promoters closed when transcription activity was inhibited, indicating a feedback mechanism between transcription and open chromatin maintenance. Our work paves the way for dissecting the complex, yet highly coordinated, epigenetic reprogramming during human preimplantation development.
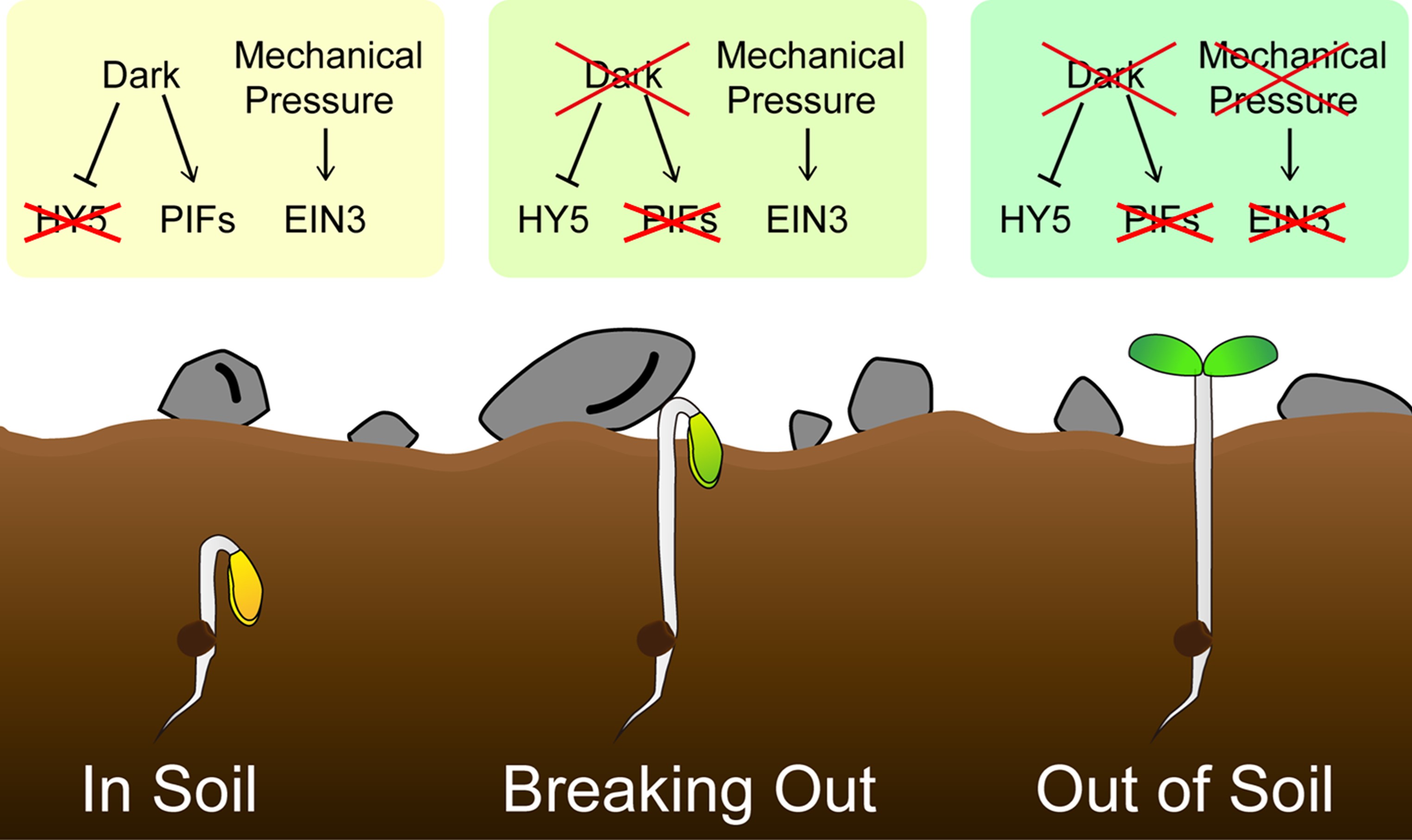 May 30,2018
May 30,2018
Seedlings of terrestrial flowering plants such as Arabidopsis display dramatically different morphologies depending on growing in the dark or light. Dark-grown seedlings exhibit long hypocotyls, apical hook formation, and closed small cotyledons with etioplast. In contrast, light represses hypocotyl elongation, unfolds apical hook, and promotes cotyledon development. How light-controlled seedling morphogenesis is regulated at the transcriptional level remains elusive. To date, three families of transcription factors—PIFs, EIN3/EIL1, and HY5/HYH—have been shown to mediate light responses in seedlings. This study systemically investigates their roles in regulating specific morphological aspects and provides both transcriptomic and genetic evidence that PIFs, EIN3/EIL1, and HY5 are master transcription factors for the proper establishment of seedling skotomorphogenesis and photomorphogenesis.